Explore the collection
Showing 8 items in the collection
8 items
Book
Hu Yaobang and the Vindication of Wrongful Convictions.
This book recounts Hu Yaobang's efforts to overturn people falsely accused of being "Rightists" during the Anti-Rightist Campaign of the 1950s. It is written by Dai Huang (1928-2016, formerly known as Dai Shulin), a Communist propagandist and later senior editor at the Xinhua News Agency, who was also persecuted in the Mao era and rehabilitated thanks to Hu's efforts.
This means that the book is not entirely objective–Dai does not analyze too closely Hu's history of slavishy following Mao's policies. Instead, he aims to capture the excitement felt by the hundreds of thousands who suffered in the Mao era and who were rehabilitated in the 1970s and '80s thanks to Hu. At 300,000 Chinese characters, or more than 200,000 English words, it is a weighty compendium that includes previously unreported details of famous public intellectuals and party members persecuted by the party and how Hu rehabilitated them. For example, Dai recounts the case of Ge Peiqi, who was a Communist Party spy who was toppled for his opposition to the party's corruption and privilege. Dai explains the case in depth and how Ge was eventually cleared.
Dai represented a liberal wing of the party that believed in the need for the party to address its mistakes. At his funeral people such as Du Daozheng (the editor of China Through the Ages 炎黄春秋) and Tie Liu (publisher of the alternative history journal 往事微痕) attended. The book also contains a preface by Li Rui, who participated in China Through the Ages and was also a mainstay of the party's liberal wing.
Book
In Search of Cannibal Witnesses
This book is part of author Eva's "Famine Trilogy." Because her mother was a survivor of the famine in Gansu, Eva has obsessively pursued and recorded that tragic history. She visited a dozen counties in Gansu and Shaanxi four times and interviewed two hundred and fifty people. The list of starving victims recorded in the book is about eight hundred and thirty, while as many as one hundred and twenty-one incidents of cannibalism and cannibalistic phenomena were recorded.
Book
In Search of Famine Survivors
This is the first book in author Eva's "Famine Trilogy," in which she traveled to Qin'an County, Tongwei County, and Tianshui District in Gansu Province as well as to Yaozhou and Tuxian County in Shaanxi Province in 2011. She interviewed more than two hundred survivors of the Great Famine, with the oldest person being ninety-five years old and the youngest being fifty-eight years old. This book allows these lowest class, mostly uneducated peasants to speak and provide their own witness, leaving behind their voices and oral history. Based on interviews with more than fifty interviewees, the book contains the names of more than five hundred victims and forty-nine incidents of cannibalism.
Book
In Search of the Fleeing Women and Children
This book is part of writer Eva's "Famine Trilogy." It is also the only oral history monograph on women and children who fled the famine in Gansu and Shaanxi from 1958 to 1963 as of now. More than 1.3 million people starved to death in Gansu Province, the hardest-hit area of the Great Famine, and more than 100,000 women between the ages of 16 - 15 years old fled the famine and left Gansu. What happened to them and their children is one of the most tragic memories of the Great Famine.
Book
My Mother :Gao Yaojie
Author Eva writes about her relationship with Gao Yaojie, a Chinese doctor. Dr. Gao Yaojie, who was severely repressed by the Chinese government for exposing the mass infection of Chinese farmers in Henan Province, China, by selling their blood, had no choice but to leave China at the age of 78 and go into exile in the United States. The dissemination of her story is strictly forbidden in China. In this book, author Eva describes Gao Yaojie's noble heart, her story, and her experiences.
Book
Rethinking China's Democracy Movement
Author Hu Ping was involved in the Xidan Democracy Wall movement in the late 1970s and now lives in the United States.
He has successively chaired the pro-democracy publications <i>China Spring</i> and <i>Beijing Spring</i>. This book, published in 1992, analyzes the reasons for the failure of the June Fourth Movement and summarizes the lessons learned. The last two chapters suggest how to continue the pro-democracy movement in the future.
Book
The Falun Gong Phenomenon
This book is a collection of several long articles and commentaries by Hu Ping on Falun Gong and the persecution and repression against Falun Gong practitioners. From an independent perspective, this book responds to a series of unfair criticisms and stigmatization of Falun Gong by the Chinese authorities and the public, calling on society to fight for the basic rights of Falun Gong practitioners who have been persecuted.
Book
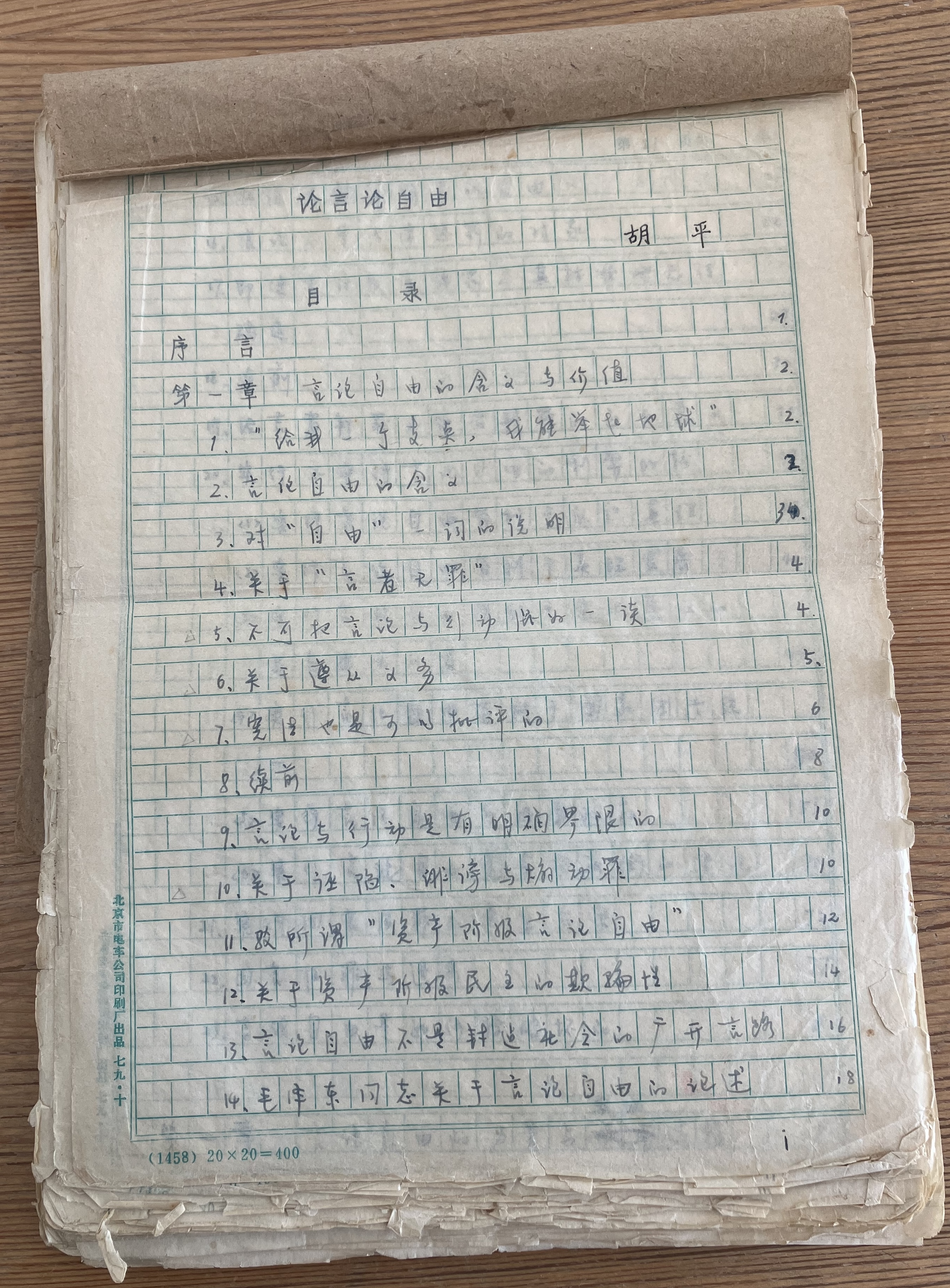
On Freedom of Speech
“On Freedom of Speech” is a treatise by Hu Ping. It was first published in 1979. A revised version was published in 1980, when Hu ran for local elections at Peking University. The treatise was later published in Hong Kong in 1981 and again in a Chinese journal in 1986. Multiple publishing houses in China made plans to distribute the treatise in book form, but China’s anti-liberalization campaign prevented the books from publishing.
“On Freedom of Speech” explains the significance of freedom of speech, refutes misunderstandings and misinterpretations of freedom of speech, and proposes ways to achieve freedom of speech in China.
This document, provided by the author, also includes the content of the symposium held after the publication of “On Freedom of Speech” in 1986, as well as the preface written by the author in 2009 for the Japanese translation of this treatise.